Since the implementation of reform and opening up, the reform and development of higher education have made significant achievements. A higher education system with various forms, which encompasses basically all branches of learning, combines both degree-education and non-degree education and integrates college education, undergraduate education and graduate education, has taken shape. Higher education in China has played an important role in the economic construction, science progress and social development by bringing up large scale of advanced talents and experts for the construction of socialist modernization.
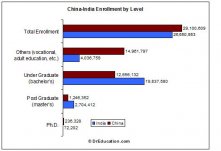
In 2010, there were all together 2305 Higher Education Institutions (HEIs), among which 1090 were universities, 322 were independent colleges and 1215 were non-university higher institutions. There were also 384 higher education institutions for adults. In 2010, the total number of new entrant admitted by and the total enrollment of the regular HEIs were respectively 5, 764, 069 and 21, 446, 570. The total number of new entrant admitted by and the total enrollment of new recruitment and total enrollment of adult higher education institutions were 316, 809 and 5, 413, 513. The total number of graduate students newly admitted by HEIs and research institutions was 332, 641 among which 23, 227 were for PhD and 309, 414 for master's degree. The total enrollment for graduate students was 1, 158, 623 in 2010.
Chinese economic system used to be very highly centralized. To adapt to that, the former higher education system was also centralized, with education provided by the central and local governments respectively and directly under their administration. The disadvantages of this system were that the state undertook too many responsibilities and the schools lacked the flexibility and autonomy to provide education according to the needs of the society, with central departments and local governments providing education separately, the structure of education was irrational and segmented. There were too many single disciplinary HEIs and professional HEIs, With the establishment of disciplines over-lapped, the efficiency of some HEIs fell very low which in return hampered the improvement of education quality. Therefore, the structural reform of higher education has become a key for other higher education reforms. The reforms of higher education consist of five parts: reforms of education provision, management, investment, recruitment and job-placement, and the inner-institute management, among which management reform is of most importance and difficulty. The overall objectives of higher education reform are to smooth the relationship among government, society and HEIs, setting up and perfecting a new system in which the state is responsible for the overall planning and macro management while the HEIs follow the laws and enjoy the autonomy to provide education according to needs of the society.
After several years' endeavor, the structural reform of higher education has gained heartening achievements. In the field of education provision reform, the old system in which the state undertook the establishment of all HEIs has been broken, and a new system in which the government take main responsibility with the active participation of society and individuals has been taking shape. The development of HEIs run by social forces are fully encouraged and supported.
Regarding management system reform, the relationship among universities, government and society has been gradually smoothed out by various ways such as joint establishment, adjustment, cooperation and merger. A two-level education provision system has taken shape in which the central and local government will take different responsibilities to provide education with the former responsible for the overall planning and management. As a result, the overlapping of education was overcome. At the same time, the government streamlines their administration and delegate more power to the HEIs, expanding their autonomy of providing education for the society according to the laws.
With regard to the financing system, the old system in which the funding of higher education depended on the governments only has been changed and a new system capable of pooling resources from diverse channels with the main responsibilities on government has been gradually established and perfected.