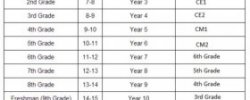
The VMBO (voorbereidend middelbaar beroepsonderwijs; literally, "preparatory middle-level applied education") education lasts four years, from the age of twelve to sixteen. It combines vocational training with theoretical education in languages, mathematics, history, arts and sciences. Sixty percent of students nationally are enrolled in VMBO. Students can choose between four different levels of VMBO that differ in the ratio of practical vocational training and theoretical education. Not all levels are necessarily taught in the same high school.
- Theoretische leerweg (VMBO-TL; literally, "theoretical learning path") has the largest share of theoretical education. It prepares for middle management and the MBO level of tertiary education, and allows students to resume vocational training at HAVO level. It was previously known as "MAVO".
- Gemengde leerweg (VMBO-GL; literally, "mixed learning path") is in between VMBO-TL and VMBO-KL. The progression route to graduation is similar to the VMBO-TL.
- Kaderberoepsgerichte Leerweg (VMBO-KL; literally; "middle management-oriented learning path") is composed of an equal amount of theoretical education and vocational training. It prepares for middle management and vocational training at the MBO level of tertiary education.
- Basisberoepsgerichte Leerweg (VMBO-BB; literally; "basic profession-oriented learning path") emphasizes vocational training and prepares for vocational training at the MBO level of tertiary education.
- Praktijkonderwijs (literally, "practical education") mainly consists of vocational training. It is tailored to pupils who would otherwise not be able to obtain a VMBO-diploma. This form of on-the-job training is aimed at allowing pupils to enter the job market directly.
At all of these levels, Leerwegondersteunend onderwijs (literally, "learning path supporting education") is offered, which is intended for pupils with educational or behavioural problems. These pupils are taught in small classes by specialized teachers.
Selective secondary education[edit]
Secondary education, which begins at the age of 12 and, as of 2008, is compulsory until the age of 18, is offered at several levels. The two programmes of general education that lead to higher education are HAVO (five years) and VWO (six years). Pupils are enrolled according to their ability, and although VWO is more rigorous, both HAVO and VWO can be characterised as selective types of secondary education. The HAVO diploma is the minimum requirement for admission to HBO (universities of applied sciences). The VWO curriculum prepares pupils for university, and only the VWO diploma grants access to WO (research universities).









 The Ministry of Education, Culture and Science (Dutch: Ministerie van Onderwijs, Cultuur en Wetenschappen; OCW) is the Dutch Ministry of Education: the position is occupied with the Dutch education policy, science policy, culture policy and the Netherlands Public...
The Ministry of Education, Culture and Science (Dutch: Ministerie van Onderwijs, Cultuur en Wetenschappen; OCW) is the Dutch Ministry of Education: the position is occupied with the Dutch education policy, science policy, culture policy and the Netherlands Public...