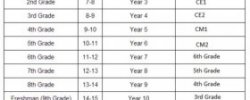
- In the past, Hong Kong education was closely modeled on the system that was found in the UK. This is hardly surprising since Hong Kong was administered by Britain from 1841 to 1997, when the former UK colony was handed back to China. However, since 1997, the education system taught in local schools has undergone a series of changes. While some of these changes have reflected different language of instruction policies, there have also been changes to the senior secondary curriculum. The new model, brought in at the beginning of the 2009/10 academic year, is now more in line with those found in China and even the USA.
While there are nine years of compulsory schooling in Hong Kong, six in primary school and three in junior secondary school, the Hong Kong government has recently moved to make it easier and more likely that the majority of students will receive 12 years of education. The removal of fees and one series of public exams in senior secondary school is a move which will make a full twelve years’ of education a much more accessible option for a great number of students.
There has always been schooling beyond the years of compulsory education. The majority of students attend 3 years of kindergarten (K1 – K3) before attending primary school. Under the new secondary system, the three years of junior secondary is followed by three years of senior secondary. This leads to the HKDSE (Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education) exams. Students gain entry to a range of post-secondary, vocational and tertiary courses offered by a variety of institutions based on the results of the HKDSE. The majority of university courses offered by Hong Kong universities will also undergo a change in structure for students graduating with the HKDSE. Many courses will become 4 year programmes, partly in response to the change from four years to three years in the senior secondary years.
The schools provided by the Hong Kong Education Department (EDB – Education Bureau) can be divided into three main groups: government schools; subsidized schools, which are usually administered by charitable bodies; and private schools run by different organizations where admission is more often decided by academic merit (schools such as DBC and DGS are example of these types of schools).
Aside from the government system, there are private independent schools. The style of education, the language(s) of instruction and the international curricula offered by these schools appeal to both expatriate and local parents. Many of these schools have waiting lists and all charge higher (and in many cases, much higher) tuition fees than local schools.
In the past, the local education system has been very exam-orientated. However, in recent years there have been some moves towards fewer exams ad more continuous and formative assessment. Schools usually have a strict discipline code and virtually all students wear school uniform.
 Primary schools used to be separated into morning (AM) and afternoon (PM) schools as a method of dealing with the problems of a lack of space and the large student numbers. However, with changing demographics and a falling birth rate, most primary schools have moved to become whole-day schools.
Primary schools used to be separated into morning (AM) and afternoon (PM) schools as a method of dealing with the problems of a lack of space and the large student numbers. However, with changing demographics and a falling birth rate, most primary schools have moved to become whole-day schools.
While most schools are co-ed, there are a number of well-known schools with good reputations which are single-sex.
Kindergartens
Since 1997, there have been changes to a lot of kindergartens as a way of professionalizing them. Most of the changes have involved minimum teaching qualifications for both kindergarten teaching staff and principals. As the government has also placed more emphasis on the importance of early childhood education, the curriculum in kindergarten has now been designed to provide a sound foundation for students.
Primary Education
The majority of local Primary schools in Hong Kong are Chinese medium of instruction and the primary curriculum covers a wide range of subjects including Social Studies, Science, Chinese, English, Mathematics, Music, Arts and Physical Education.
Students are allocated to Secondary schools through their performance in three examinations taken in Primary 5 and Primary 6. Schools are extremely competitive and parents naturally have a strong preference for their child to be allocated to a top or higher band school.
Recently, primary school numbers have been shrinking, causing the closure of some schools and resulting in the need for some teacher redundancies.
Class numbers are traditionally much higher in Hong Kong than they are in Western countries. An average class, in both primary and secondary school could have over 35 students and it can be as many as 45. The shrinking enrollments have seen a lot of debate about smaller class sizes but so far the numbers of students in a class have not been greatly reduced.
Secondary Education
The first year of secondary school, known as Form or Secondary One, follows six years of primary education. Forms 1 – 3 have compulsory attendance and in junior secondary, the learning is broader, without students choosing specific study areas.
The majority of local secondary schools became Chinese medium of instruction (CMI) after the Handover in 1997. However, since then many have gone back to an English medium of instruction (EMI). In 2013, 112 out of 400 secondary schools are EMI.
Students in Forms 4-6 now prepare for the HKDSE, the examinations for which are held at the end of Form 6. There are four core subjects – English, Mathematics, Chinese and Liberal Studies. Students then choose two or three elective subjects from a choice of 20. There are also some applied learning subjects, modeled on the idea of the BTEC and six other modern foreign languages which can also form part of the students’ choices.
how long startup repair windows 7 where did we come from science how much product manager salary how much develop film philippines whose team how to roadmap in jira where the solutions to the identified problems presented where to project x when project tiger was launched why tech sales how to find device without location who manufacturers the flu vaccine where to go from business analyst why roadmap is important why solution of na2co3 is alkaline who roadmap meningitis 2030 who buy products and who use product where is my product from what manufacturer makes infiniti where to find system configuration whose science whose knowledge pdf who managers real madrid how london became the center of the world where is development length what solutions conduct electricity how science goes wrong how to start online startup how many management levels in ges which design pattern to use who design nazi uniforms in startup who ends up with who when design user interface how many engineering degrees are there how much factory unlock iphone 6 whose business are you in where system earthing is employed how start up a business how much science is required for upsc where to get business license who solution for covid 19 how many equipment in an equipment deck who owns positive solutions how startup valuation works which science is easier in college what engineering is the easiest where to manage kindle unlimited where is sany equipment from where to solve math word problems why london is a good place to live who developed the hierarchy of needs which entrepreneur is associated with the financial industry how much project management cost whose business is best how often to maintain muscle how science is unlocking the secrets of addiction where to set up signature in outlook where teaching and learning come together what business should i start quiz which science is the most important who design washington dc which engineering has highest salary how management works why teaching is the hardest job how system call works in linux where is derby from london how much engineering make who project pdf how much phone screen repair what engineering should i major in where to recycle technology where are workers going from where was solar system originated how much design for architect where business intelligence is used how many entrepreneurs are in the world where's the london bridge in arizona how product managers work with data scientists how often phone upgrade how manager handle conflict how device tree works startup folder why london is so expensive where science has lease where project nasa how to roadmap an essay what solutions are neutral london who started the great fire how engineering works why management information system is important where to find device management on iphone who company owns snapper mowers where to solve word problems who studies science where is working solutions located how device is rooted where design thinking is used where to watch project x why system ui isn't responding what manufacturer makes infiniti who management of pain how many equipment are used in rhythmic gymnastics where to donate technology near me why equipment is important in harvesting crops where to buy technology how many workers make minimum wage which equipment is exclusive to kevesi soldiers how solution is prepared what system is the gallbladder in how much tech trash for c4 what startup apps do i need why science is wrong how many equipment lost in where is aiken product from whose manager of salford city what start up business how much solution in little green machine where teachers get paid the most where to manage friends lists on facebook