High school/secondary school? University/college? A-levels/SATS? Explore the differences and similarities in the academic journey of students in the US and UK.
On the whole, the education of British and American students is fairly similar – they all start compulsory schooling between the ages of 5 and 6, then finish 12 years later. There are however, a few fundamental differences.
We’ve designed a 12 Years a Student infographic that charts their journey from birth until graduation.
Click on image above to view the full 12 Years a Student infographic!
British schools! American schools!
There was only so much we could fit on the infographic, so here are a few more UK and US student facts…
In the UK, ‘public schools‘ are what Americans call ‘private schools‘. This can be quite confusing because ‘public’ implies a communal state education system open for all, but in the UK these schools tend to be privately funded fee-paying schools.
In the UK, if someone says they are ‘going to school’ it means they are attending an academic institution for those aged between five and eighteen. In the US, it means a place of higher education (university).
In the UK, the word ‘college‘ is used to describe academic institutions for those aged 16 to 18 (those studying their A-Levels). In the US, the word ‘college‘ refers to a place of higher education (university).
Similar to the US meaning, however, the UK also use the term ‘college‘ to denote schools within a university – for instance the University of London has different colleges within it which are also universities in their own right.
- FYI, in the UK the word ‘university’ is commonly abbreviated to ‘uni‘.
In the UK, when someone says they are ‘going on holiday’ it is the US equivalent of ‘going on vacation’. A ‘holiday’ in the US tends to be a national holiday, which is called a in the UK.
The term ‘secondary school‘ in the UK is used to denote the academic years from ages 11 to 18. In the US the similar term would be ‘high school‘ for those aged 14 – 18.
In the UK when students are in their last two years of secondary school education they take exams known as ‘A-Levels‘ – these are university entrance exams similar to ‘SATs‘ in the US. Students typically take 3 or 4 A-level subjects.
In the UK, during your first year at university you will be referred to as a ‘fresher‘. In the US you will be called a ‘freshman‘.
As well as the term ‘freshmen’, the US also use terms to describe the subsequent years – ‘sophomore‘, ‘junior‘, and ‘senior‘ (aka: second year, third year and fourth year).
- FYI these US terms are also used in the four years of high school.
When you’re ready to start applying for jobs in the UK, you will need to create a ‘CV‘ (short for the Latin, Curriculum Vitae). In the US this is called a ‘résumé‘.
The word ‘mark‘ in the UK has the same meaning as ‘grade‘ in the US i.e. ‘what grade did you get in your test?‘
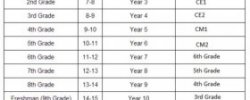
Additionally in the US, the word ‘grade’ is used to refer to the academic year that a student is in i.e. ‘what grade are you in?‘ is the same as saying ‘what year are you in?‘ in Britain.
Americans use the word ‘major‘ to signify the main subject they are studying at university. It is similar to the word ‘degree’ in the UK.
- US: I’m majoring in biology
- UK: I’m studying a degree in biology
A double major in the US is essentially the study of two subjects. In the UK this is the equivalent of a joint honours degree course (50%/50%).