Academic prerequisite
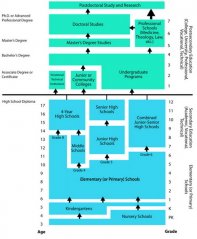
Admission requirements vary between universities and colleges in the United States. You normally must have graduated from secondary school (called high school in the US). You must also fulfill the requirements for the specific education course to which you are applying. In addition, most schools require results from a test like the SAT Reasoning Test (Scholastic Assessment/ Aptitude Test), which is a standardized test for university admissions.
Linguistic prerequisite
Some schools in the US accept that you have obtained certificates at sufficiently high standard in English from secondary school. Other universities require that you complete a TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language) or IELTS (International English Language Testing System) test to prove your English skills.
Grading System
Almost everything you do for a class in the United States will effect your grade: examinations and tests, essays or written assignments, laboratory reports, studio work, class attendance, and class participation.
The grade scale is usually from either A to F or 0-4. For each grade, you need certain percentages. For example, to get an A (or 4) on a test, you usually need to correctly answer 90-100 % of the questions, to get a B (or 3), you need 80-90%, and so on. Other common grades are:
• I = incomplete
• W = withdrawal
• Audit = enroll in the course for no credit or grade, but attend class and complete assignments
• Pass/ Fail = enroll in the course for either a Pass or a Fail grade
• Pass/ No Credit = enroll in the course for either a Pass or a No Credit grade, with no negative points
Examinations are usually given once in the middle of the term and once at the end. Professors often give short quizzes or tests inbetween, with or without notice. Many times you must write a research paper or complete a project assignment toward your final grade.
An additional resource for students who are interested in studying in the United States is the Grade Conversion Guide. With this guide, students can compare grades in the United States with those of other countries, making it easier to understand entry requirements and determine for which programs they may be eligible.
Credit System
Each course you take at a university in the USA is counted as a certain number of credits, also called hours or units. You normally need between 130 and 180 credits to graduate. One credit is equal to 50 minutes of class time per week; completing a class that meets 3 times every week is equal to earning 3 credits. Full-time students usually earn 15 credits every semester. Students are assigned an academic advisor at the school who helps plan their credits and courses.
Semester System
Most schools in the USA have a two-semester system, each semester lasting for roughly 15-17 weeks. The fall semester usually starts in late-August or September, and finishes just before or after Christmas. The spring semester begins in early- to mid-January and runs until May or sometimes June.
Some schools in the United States use a semester system called the quarter system, each quarter lasting for about 10 weeks. There are also schools which schedule three-semester academic years, where each semester is 10-12 weeks.
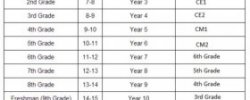
The 'years' at American higher educational institutions are as follows:
- Freshman: 1st year
- Sophomore: 2nd year
- Junior: 3rd year
- Senior: 4th year