The Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) in Poland are divided into state (public) and private (non-public) institutions. There are two main categories of higher education institutions: university-type and non-university institutions. In the university-type HEIs, at least one unit is authorised to confer the academic degree of Doctor (PhD), i.e. offers at least one doctoral programme.
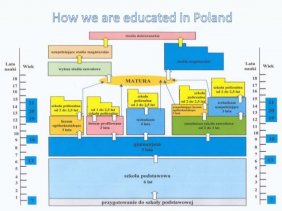
Structure of studies in Poland
The higher education institutions run full-time, extramural, evening and external courses. The full-time courses are defined as the basic type of studies.
Poland conforms to the guidelines from the Bologna Process in European higher education. The degree system based on the three-cycle structure has been successfully implemented together with the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS). The European standard in higher education makes it easier for students to obtain recognition of their qualifications in other countries.
1st Cycle
First-cycle studies (3 to 4 years) leading to the professional title of a licencjat or inżynier (Engineer, in the field of engineering, agriculture or economics). This is the Polish equivalent of the Bachelor’s degree. It is focused on preparing students for future employment or for continued education within the Master’s degree programmes. To obtain this degree, students must earn 180-240 ECTS credits.
2nd Cycle
Second-cycle studies – Master’s degree programme (1.5 to 2 years) following the first cycle studies and leading to the professional title of Master (magister, or an equivalent degree depending on the study course profile). It is focused on theoretical knowledge as well as application and development of creative skills. In artistic disciplines, the focus is on the development of creativity and talents. Master’s degree holders may enter a doctoral programme (third-cycle studies). To obtain the degree, students must earn 90-120 ECTS credits.
Long-cycle studies
In addition to the general structure, 11 fields of study including acting, art conservation and restoration, canon law, dentistry, law, medical analysis, medicine, production and photography, pharmacy, psychology and veterinary medicine, offer long-cycle programmes only.
Long-cycle studies – Master’s degree programme (4.5 to 6 years) leading to the professional title of Master (magister, or an equivalent degree depending on the study course profile). To obtain this degree, students must earn 270-360 ECTS credits. Such single long-cycle studies are based on an integrated study programme which contains both basic studies and in-depth specialisation. Completion of this degree will provide a qualification corresponding to the Master’s degree at the second-cycle studies.
3rd Cycle
Third-cycle studies – Doctoral degree programmes (normally 3 to 4 years) accessible for graduates of Master’s degree programme, leading to a PhD degree, offered by the university type schools as well as some research institutions (departments of the Polish Academy of Sciences as well as research and development institutions). The PhD degree is awarded to candidates who submit and successfully defend a doctoral dissertation before the thesis committee and pass the doctoral examination.
Examinations
All higher education institutions are required to end their courses with examinations. There may be several independent examinations or tests in separate parts of a subject. Usually, oral and written examinations are held at the end of each semester during the examination session. Students sit examinations on each subject separately. The performance assessment period covers either one semester or one academic year. To successfully complete a semester (or a year), a student must attain the pass mark (at least “satisfactory”) for all assessments and examinations in the subjects covered by the curriculum and obtain performance assessment credits for all integrated placements.
Grading: Each HEI identifies its grading scale in its Study Rules. The most common scale comprises the following marks:
5 very good (bardzo dobry)
4 good (dobry)
3 satisfactory (dostateczny)
2 unsatisfactory/fail (niedostateczny)
credit/pass (zaliczenie)
Sometimes the plus symbol or decimal is used to modify the numerical grades.
It must be pointed out at this time that grades awarded according to the scale are not directly transferable to the ECTS credits.
ECTS credits
In addition to the grading scale, there are HEIs in the European Credit Transfer System (ECTS) under which a certain number of credits is allocated to a given subject, independently of marks awarded. To complete a year successfully, the student has to collect 60 credits (30 per semester).
The ECTS (European Credit Transfer System) is the standard adopted by all universities in the European Higher Education Area (EHEA) in the process of convergence between Europe’s higher education systems. Since 2007, all Polish higher education institutions have been required to use ECTS for both credit transfer and accumulation within their degree programmes. The ECTS credits allow foreign students’ periods of study at HEIs in Poland to be recognized.
For more information on the adjustment to the Bologna Process and ECTS credits please visit: (European Higher Education Area); (The Bologna Process, official website).
Diploma
In order to graduate, students are required to:
- pass a performance assessment for all subjects, integrated placements and practical work sessions, and pass all examinations covered by the study programme set for a given field of study;
- present, at an appointed date, a diploma project and attain a pass mark for that project;
- pass the diploma examination.
Upon graduation, the student receives a diploma of completion of studies in a specific field of study together with a Diploma Supplement (copy of the diploma translated into a foreign language, describing the degree, level and specialisation).
https://globalapostille.us, apostille documents. Florida apostille.