There are so many different types of schools that the options can seem overwhelming. To help you figure out which colleges and/or career schools might be best for you, we provide descriptions of the main types of schools and the average time it takes students to graduate.
There are so many different types of schools that the options can seem overwhelming. To help you figure out which colleges and/or career schools might be best for you, we provide descriptions of the main types of schools and the average time it takes students to graduate.
(also known as technical or vocational schools)
Public or Private?
Public schools are operated or funded by state and local governments. Private schools are not affiliated with a government organization. They may be nonprofit colleges, such as those run by private foundations or religious denominations. Or, they may be for-profit businesses, such as many career, online, or technical schools.
Since private schools receive less (or no) money from state and local governments, they usually cost the same whether you live in or outside of the state. This cost is often higher than the cost of attending a public school in your state.
Because costs can vary significantly from school to school, you should make sure to research the schools you are interested in. Any school that participates in the federal student aid programs is required to provide information on its cost of attendance on its website. The school is also required to provide a net price calculator which will give you an idea of how much a program may cost after subtracting any financial aid.
Four-year Colleges and Universities
Students who attend a four-year college or university typically earn a bachelor’s degree once they have successfully completed a program of study, which usually takes about four years.
A college usually offers a four-year bachelor’s degree in the arts (such as English, history, drama) or sciences (such as biology, computer science, engineering). Some colleges also offer advanced degrees, such as master’s or other graduate degrees, after you’ve earned your bachelor’s degree.
Universities offer bachelor’s, master’s, and doctorate degrees, and sometimes have professional schools such as a law school or medical school. Universities tend to be larger than colleges, may have larger class sizes, and often focus on scholarly or scientific research.
 Two-year Colleges (Community and Junior Colleges)
Two-year Colleges (Community and Junior Colleges)
Community colleges and junior colleges award associate degrees once students have successfully completed a two-year course of study. Some two-year colleges grant diplomas or certificates of completion to students who have met course requirements and are ready to practice in their career fields, such as nursing. Community and junior colleges are similar, except that a junior college is usually a private school.
Because costs are often lower and admission is more open at two-year colleges, many students begin their college careers here. If you plan to start at a community or junior college and later transfer to a four-year college, you should make sure your community college courses will transfer to those colleges you are interested in and that your courses will count toward your bachelor’s degree. Many community colleges have “articulation agreements” with four-year colleges under which the course work taken at the community college transfers into the four-year degree program. Be sure to ask about the types of articulation agreements the community college has, with whom, and for what programs of study.
Career Schools
Career schools, also known as technical, vocational, or trade schools
- may be public or private, although many are for-profit businesses;
- typically offer programs that are two years or less; and
- provide students with formal classes and hands-on experience related to their future career interests, from welding to cosmetology to medical imaging.
Technical schools teach the science behind the occupation, while vocational schools focus on hands-on application of skills needed to do the job. You may earn a diploma or a certificate, prepare for a licensing exam, or study to begin work as an apprentice or journeyman in a skilled trade.
Some schools offer distance learning, which allows you to access lectures or course materials online or through other electronic media. Since not every distance learning course or online degree is accredited and/or eligible for federal student aid, check with the school’s financial aid office to find out whether you can receive federal aid.
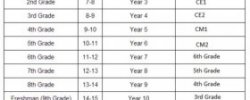
Graduation Time by Program or Degree and Type of School
|
Program or Degree |
Schools Where Offered |
Typical Time to Graduate |
|---|