A secondary school in the United States might also be known as a high school or as an academy. It usually provides educational instruction for students during the period from ages 11 to 18. Read on to learn more about secondary schools.
Secondary School Grade Levels
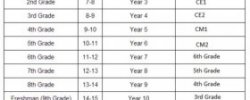
A secondary school in the U.S. commonly consists of grades 9 through 12, with grade levels known as freshman, sophomore, junior and senior, respectively. Some larger school districts fund secondary schools that teach only grades 10, 11 and 12. Some secondary schools include students in grades seven and eight, along with the higher grade levels. Secondary schools represent the final stage of compulsory schooling in most U.S. states. State law proscribes school attendance until graduation or until a specific age, whichever comes earlier.
Important Facts About Secondary School
| Degrees/Certificates | High school diploma or GED |
| Continuing Education | Bachelor's Degree, professional certification |
| Common Courses | Biology, geometry, fine arts, foreign languages |
| Online Availability | Accessible through a variety of national programs |
General Academic Secondary Schools
Most high schools offer a range of general academic courses. The curriculum usually includes courses such as English, mathematics, science, history and a foreign language. Other common subjects offered during high school include industrial arts, homemaking, health, physical education and music. Students may distribute curriculum selections between required classes and electives.
Other Types of Secondary Schools
Other high schools are classified as comprehensive secondary schools. Comprehensive schools may provide specialized training so that students can transition into vocational or technical professions after graduation. College preparatory schools focus on students who plan to enter colleges or universities after graduation. Special or alternative high schools may enroll students who seek intensive fine arts instruction or those who may need child care while attending classes.
Funding for Secondary Schools
U.S. high schools are typically supported by local, state and some federal funds. The proportion of funding from each funding source varies from state to state, according to the Digest of Education Statistics from the U.S. Department of Education (www.ed.gov). Privately funded high schools may be supported by religious institutions or by other contributions.