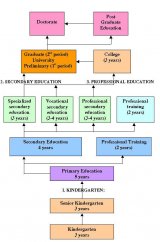
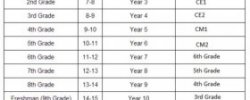
Secondary education in the UK normally starts for most students at the age of 11 years old. Though not common, in some parts of the UK there are middle schools which run up to 12 or 13 years old.
For international students coming into the UK for secondary education, it is common to either enter at the age of 11 or wait until the age of 13 and have one year in the school before starting the two-year GCSE program which will run from 14 to 16 years old.
From the age of 11-14, students will study a broad range of subjects such as Music, Maths, Sciences, English, etc. When you reach 14, you generally enter into your first year of a 2 year process known as your GCSE (or SCE for those who are in Scotland). GCSE's are a set of exams that test your knowledge and skill.
Most schools follow the same method when it comes to GCSE's and you will take the following core subjects:
- English
- Maths
- Sciences (either combined or separate Biology, Chemistry and Physics)
Students typically then select an additional 4 or 5 subjects in which to take GCSE's, and they can be subjects like French, German, Business Studies, Design and Technology, Music, Sports Science, Geography, History and many other options.
At state schools students typically take 5 to 10 GCSE's, depending on the student's ability and drive. For independent schools, which are usually a lot more results driven, it is not uncommon for students to take as many as 11 or 12, focusing more on academic subjects compared to the arts subjects.
GCSE's take a total of 2 years and mark the end of compulsory education for students in the UK. Once they have completed their GCSE's students then have the choice to either move into further education (with a view to higher education) or can leave school and look for work.