Search
Us school grades
Sign up to get Your Wealth Please enter a valid email address All three states made financial education mandatory after 2 and previously had not required...
Read MoreUniversities in Warsaw, Poland

Why UW? A high-ranking university 2014 – the University of Warsaw was declared number 1 in Poland in scientific ranking published by the POLITYKA weekly;...
Read MorePrimary schools in USA

Elementary education starts at the age of five or six, depending on the particular state and whether a kindergarten (K) year is provided. Even when provided...
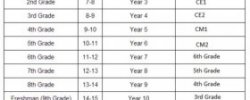
Read MoreUS high school grades

In the United States, students usually begin a formal educational program around age five or six in kindergarten. Children then complete grade levels one...
Read More